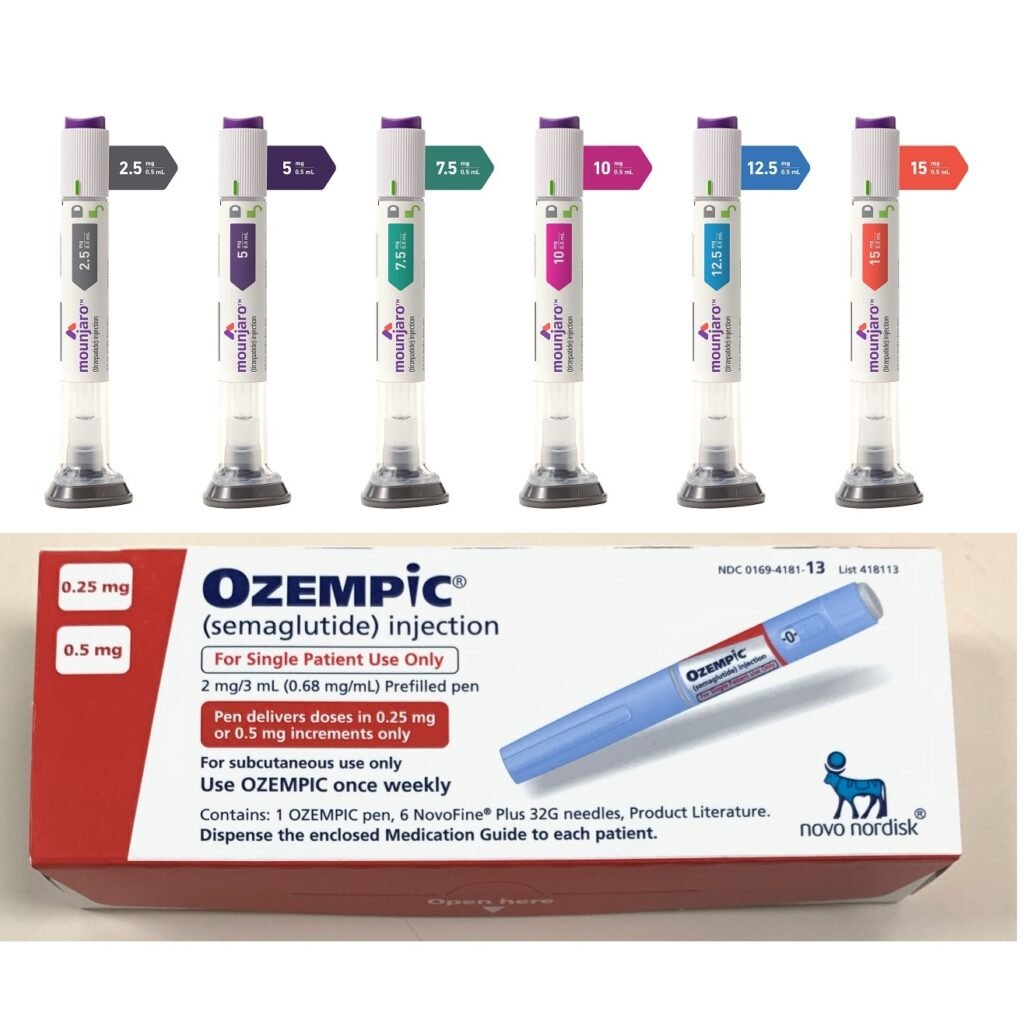
Mounjaro vs Ozempic: Choosing the Right GLP-1 Medication for You
Mounjaro and Ozempic are both popular GLP-1 receptor agonists used to manage type 2 diabetes and aid in weight loss. While they share some similarities, they also have key differences you should consider when choosing the right medication for you.
Table of Contents
What are the similarities between Mounjaro and Ozempic
- Mechanism of action: Both Mounjaro and Ozempic mimic the incretin hormone GLP-1, which stimulates insulin production, reduces glucagon release, and slows down appetite.
- Effectiveness: Both are effective in lowering blood sugar levels and managing type 2 diabetes.
- Administration: Both are injected medications, typically used once weekly.
- Side effects: Both can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and low blood sugar.
What are the differences between Mounjaro and Ozempic
- Target molecules: Mounjaro targets both GLP-1 and GIP (gastric inhibitory polypeptide) receptors, while Ozempic only targets GLP-1.
- Weight loss: Studies suggest Mounjaro may be slightly more effective for weight loss than Ozempic. Source
- Cardiovascular benefit: Ozempic is FDA-approved to reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in adults with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease. Mounjaro does not yet have this approval.
- Dosage options: Mounjaro has more dosage options than Ozempic, providing greater flexibility for individual needs.
- Cost: Mounjaro and Ozempic both without insurance coverage cost over $1000 in US. If insurance cover these medications then both can cost anywhere from $0 to $25 for each month. With Mounjaro and Ozempic coupon without insurance currently Ozempic is more expensive for patients.
Mounjaro and Ozempic in Tabular Comparison
| Features | Mounjaro | Ozempic |
| Target molecules | GLP-1 and GIP receptors | GLP-1 receptor only |
| Primary use | Type 2 diabetes and weight loss | Type 2 diabetes |
| Weight loss effectiveness | May be slightly more effective | Effective |
| Cardiovascular benefit | Not yet approved for this indication | FDA-approved to reduce major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in specific patients |
| Dosage options | More dosage options | Fewer dosage options |
| Cost | More expensive | Less expensive |
| Prior authorization criteria | Generally similar to Ozempic, but additional criteria may apply due to weight loss indication | Primarily focused on type 2 diabetes diagnosis and treatment history |
| Side effects | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, low blood sugar (similar to Ozempic) | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, low blood sugar |
| Administration | Injected once weekly | Injected once weekly |
Which is better Ozempic or Mounjaro
Which one is right for you?
The best medication for you depends on your individual health conditions, goals, and risk factors. Let’s see how you want to proceed with this question in your mind
Choose Mounjaro if:
- You’re looking for a medication that may be more effective for weight loss.
- Additionally if you have prediabetes or early-stage type 2 diabetes.
- You need more dosage flexibility, since mounjaro comes in 6 different strengths/variations.
Choose Ozempic if:
- You have type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease.
- You’re primarily concerned about controlling blood sugar and managing diabetes.
- You’re looking for a more affordable option.
- At present Ozempic insurance coverage for type-2 diabetic patients is more than Mounjaro in US. Ozempic is a preferred drug with several insurances compared to Mounjaro that goes in Prior Authorization (P.A.) with several insurances.
Ultimately, the best decision is made in consultation with your doctor. They can assess your individual health, weigh the risks and benefits of each medication, and recommend the one that best suits your needs.
Mounjaro prior authorization criteria
1. Diagnosis:
- Type 2 diabetes: Most commonly, Mounjaro requires a confirmed diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. Some plans may consider it for prediabetes with specific risk factors.
- Obesity (BMI ≥ 30): For non-diabetic patients, some insurance companies may cover Mounjaro based on a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 30 or higher.
- Comorbidities: In some cases, having additional conditions like sleep apnea, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, or polycystic ovary syndrome can support Mounjaro coverage.
2. Treatment history:
- Failure of other medications: Insurance providers want to see evidence that you’ve tried and failed to control your condition with other available medications, demonstrating Mounjaro’s necessity.
- Dietary and exercise efforts: Documentation of attempts at lifestyle changes like healthy eating and regular exercise can strengthen your case for Mounjaro as an additional support measure.
3. Specifics of Mounjaro use:
- Dosage and duration: Insurance companies may request justification for the chosen dosage and treatment duration. Being prepared to discuss your doctor’s rationale can be helpful.
- Contraindications and allergies: Addressing any potential contraindications or allergies related to Mounjaro can ease any concerns the insurance company might have.
Ozempic prior authorization criteria
Ozempic, a popular GLP-1 receptor agonist, can be a powerful tool for managing type 2 diabetes and aiding in weight loss. But like many effective medications, obtaining prior authorization from your insurance company might be required. Knowing the criteria behind that decision can streamline the process and improve your chances of approval.
1. Diagnosis:
- Type 2 diabetes: Ozempic is primarily approved for treating adults with confirmed type 2 diabetes. Some plans may consider it for prediabetes with specific risk factors.
- BMI ≥ 35: For non-diabetic patients, some insurance companies may cover Ozempic based on a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 35 or higher.
- Comorbidities: Having additional conditions like cardiovascular disease, fatty liver disease, or sleep apnea can support Ozempic coverage in some cases.
2. Treatment history:
- Failure of other medications: Insurance providers likely want to see evidence that you’ve tried and failed to control your blood sugar or weight with other available medications before approving Ozempic.
- Dietary and exercise efforts: Documentation of attempts at lifestyle changes like healthy eating and regular exercise can strengthen your case for Ozempic as an additional support measure.
3. Specifics of Ozempic use:
- Dosage and duration: Insurance companies may request justification for the chosen dosage and treatment duration. Being prepared to discuss your doctor’s rationale can be helpful.
- Contraindications and allergies: Addressing any potential contraindications or allergies related to Ozempic can address any concerns the insurance company might have.
Tips for smooth sailing:
- Consult your doctor: Work with your doctor to gather documentation like medical records, lab results, and treatment plans demonstrating your need for Ozempic.
- Understand your plan: Familiarize yourself with your specific insurance plan’s prior authorization criteria for Ozempic. You can usually find this information on their website or by contacting customer service.
- Appeals process: If your initial request is denied, be aware of your plan’s appeals process. You can typically submit additional information or have your doctor directly advocate for your case.
- Communication is key: Maintain clear and open communication with your doctor and insurance provider throughout the process.